Leaked data from a real Pixel 6 Pro drive suggests that the included Google Tensor chip may be one of the fastest chips available for Android phones.
Earlier this year and well above expectations, Google formally introduced the Pixel 6 and Pixel 6 Pro announcing the Google Tensor chip that will be found on phones. When Google has previously upgraded its phones with components such as the Neural Core, which processes photos and manages some functions of the Google Assistant, and Titan, its dedicated security hardware, the Tensor chip will integrate them into its own design to get more efficiency.
While Google is surprisingly open about the Tensor chip and its improvements, the company has left many details unshared. For example, we don’t know the chip’s performance against competitors from Qualcomm, Samsung or even Apple.
Over the weekend, a list of the “Pixel 6 Pro” appeared on Geekbench, a common tool for comparing computers and smartphones that shares many of the specifications of this device. While this may seem like a gold mine (and for a while, it was), people were quick to start making fake “devices,” posting the results, and seeing how the outlets referred to them as “leaks”.
It even proves it another The same day the Geekbench list for the “Pixel 6 Pro” was released, which appears to have a Qualcomm processor, an obvious contradiction and falsification. Because of how easy it can be to falsify these lists, you need to take them with a grain of salt.
That said, the people at XDA cite a source with a real Pixel 6 Pro model in hand. According to reports, this source was able to corroborate some of the details of the most plausible Geekbench listing, along with many other details of Pixel 6, including some details about the Google Tensor processor that will debut in the Pixel 6 series. The crucial details about the compatible source with the Google Tensor XDA chip are the layout of the processor cores and their frequencies, which together are enough to baffle the entire design.
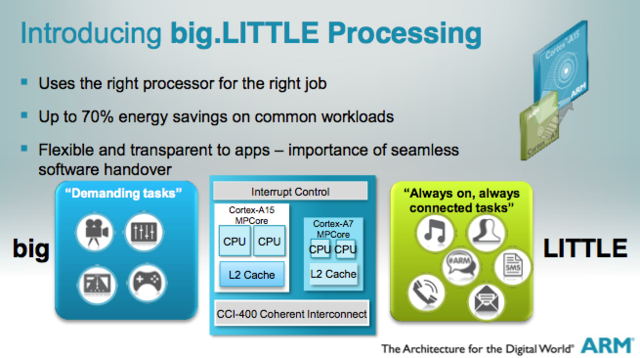
For years, most ARM processors on smartphones conformed to a “big.LITTLE” design that used a more powerful (or “large”) core cluster for demanding applications / games, while a core cluster low-power (or “low-power”) has handled the rest of the phone’s needs. This has provided a strong balance between being able to get high performance at one time and providing good battery life the rest of the time.
More recently, chip designers have decided to add a third cluster to the mix. Both Samsung and Qualcomm have chosen to use what we will call a “1 + 3 + 4” design, ie a cluster with a high-power core, another with three medium / large cores and a third with four low-power nuclei. The Snapdragon 888, for example, uses a single-core Cortex-X1 for its high-power cluster.
Meanwhile, if you can believe the corroborated list of Geekbench, the Google Tensor chip of the Pixel 6 shifts things more to high power activities, with a “2 + 2 + 4” configuration. Specifically, the frequencies used and the hidden details of the Geekbench listing point to two Cortex-X1 cores, two Cortex-A78 cores in the middle slot, and four Cortex-A55 cores for the lower part. Compared to the Snapdragon 888 and Exynos 2100 processors, the difference is one less A78 core in exchange for a second X1.
As explained when the Cortex-A78 and Cortex-X1 were announced, the two are quite similar in design, but when the A78 balances performance and energy efficiency, the X1 is based on the gross yield, offering about a 23% increase.
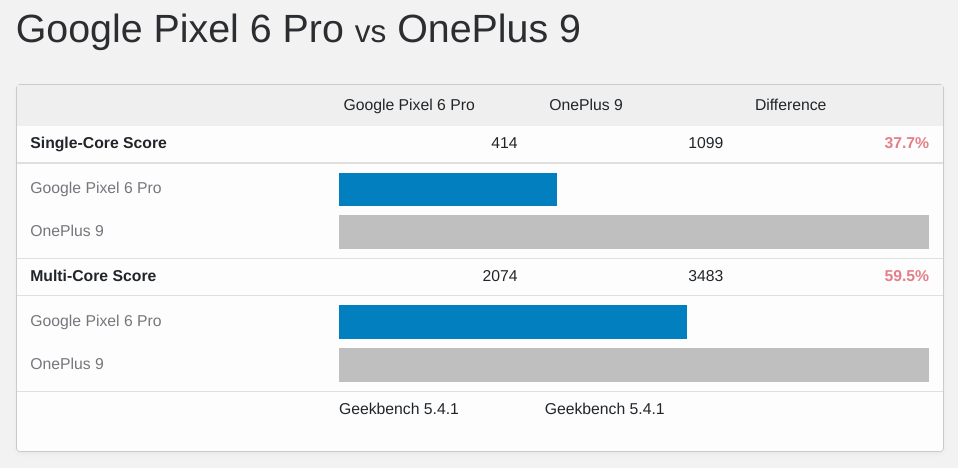
While it’s hard to say without doing so, all indications are that the Pixel 6 is faster than current Snapdragon 888 phones because of the Google Tensor chip, if it may cost energy efficiency. Conversely, however, according to Geekbench benchmarking, the Pixel 6 Pro got a much lower score than phones with the Snapdragon 888. The low score may be just a mistake, or the list may be completely false. .
If this leak is met, this would be a major correction to the course of the Pixel series. Last year’s Pixel 5 opted for a higher-end mid-range processor that helped Google create an affordable flagship. Even before, Pixel phones, typically released ten months after each generation of Qualcomm chips and two months before the next generation, used to be at the expense of other companies ’phones.
Between the significantly improved machine learning performance of the Cortex-X1 and the built-in TPU (tensor processing unit) of the Tensor chip, it’s clear that Google maintains the emphasis on making Pixel phones excellent thanks to its machine learning ability. The biggest difference this year is that the Pixel 6 and Pixel 6 Pro will have the raw computing power to do these tasks quickly, unlike the Pixel 5, which left the neural core behind.
We’ve already seen visions of what Google can do with the power of the Tensor chip, beyond faster image processing, in features such as “Quick Phrases” for the Google Assistant. We’ll probably learn more about how Google will distinguish the Pixel 6 series from other Android smartphones by the time it launches this fall.
Learn about Pixel 6:
FTC: We use auto-affiliate links with revenue. Month.
Check out 9to5Google on YouTube for more news: